FR0054 Potez 25 Salmson 18 CMb
History:
Henry Potez created the Société des Avions Potez in 1921 after working with Marcel Bloch in the S.E.A. during WWI. He assigned the design of the Potez 25 to Louis Coroller. Of mixed wood & metal construction and powered by a 450 ch Lorraine-Dietrich 12 Eb engine, the Potez 25 prototype is thought to have first flown early in 1925.

The first prototype (25.1) was transferred to S.T.Aé in 1925 for testing, whilst an unarmed prototype (25.2) made a tour of European countries to demonstrate the viability of the design. This indicated the need for some modifications, the most significant being an increase of the wingspan to 14.16 m.
The Potez 25 was one of the most widely built French aircraft between the World Wars. Most aircraft were powered by Lorraine 12 Eb, Hispano-Suiza, or Gnome-Rhône (a licence-built Bristol Jupiter) engines, whilst some used Renault, Farman, or Salmson power. Either Potez or Messier landing gear was fitted and three styles of tailfins employed. This very versatile design was operated by about 20 countries and was still in use at the outbreak of WWII.
The Potez 25, in its various engines, was used by the following countries: France (several hundred), Poland, Romania, Abyssinia, Manchuria, Japan, Paraguay, Portugal, Uruguay, Yugoslavia, Brazil, Estonia, Finland, Switzerland, Guatemala, Greece and Spain. It wass also used by Aéropostale in South America to cross the Andes (two modified A2s with Lorraine engines, three others in a modified TOE version). It was built under license by Yugoslavia, Romania and Portugal. The Potez 25 was used in conflicts by Paraguay (Chaco War), Greece, Yugoslavia, Japan, Brazil and France, where some aircraft were still being employed in 1940 in schools or for liaison work.
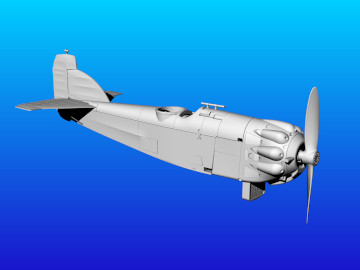
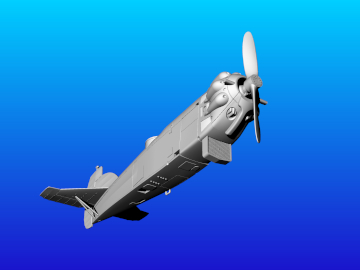
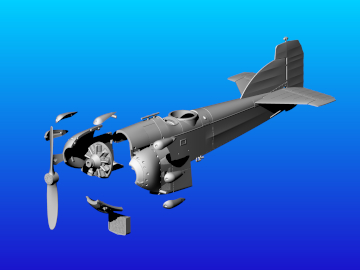
The Salmson 18CMb engine was unusual being a water-cooled radial (most radials being air-cooled) with 18 cylinders giving 520 ch, which was slightly more powerful than the Lorraine 12Eb. 270 Potez 25s A2/B2s were ordered with this distinctive 18CMb engine. These aircraft had a new more rectangular tail-fin whose shape made it readily identifiable. A number of these aircraft were assigned to the 38th RAM, based at Thionville, one of this unit’s squadrons used the Gaul's head badge, which in its second iteration was inspired by the logo used on cigarette packets at that time.
The prototype of the first Potez 25 Salmson (P25.24) was modified for long-range raids, with an additional teardrop-shaped fuel tank under the second seat, this position had its machine-gun ring removed and was moved further back in the fuselage. Labaurie and Sahuc crewed this machine.
Possibly as many as 16 Potez 25s were powered by Salmson 18 Ab engines, these had a very different appearance from the 18 CMb as they were conventional air-cooled twin-row radials.
A few Salmson-powered Potez 25s were converted for civilian use, two confirmed registrations being F-AOMG (18CMb) and F-AMQD (18 Ab).
Several Salmson 18 CMb-powered aircraft were delivered to Spain’s Republican Government during the civil war, with at least one of these aircraft serving with Grupo 71.
Specifications (Salmson 18 CMb): reconnaissance (A2) and bombing (B2) biplane. Salmson 18 CMb 18-cylinder radial engine rated at 520 ch. Wingspan 14.16 m, length 9.61 m. Armament: 1 fixed Vickers machine gun, 2 Lewis machine guns on TO7 mountings, 1 ventral Lewis machine gun.
Schemes and decals :
- The below schemes are not totally accurate, the landing gear was in all these cases a Messier (parts C57 et C58), not the Potez (parts C44 and C45) as shown. However, building instructions are right.
- N°207, 2 ème escadrille, GB I/38, Mourmelon, June 1929 (badge "Gaul's Head" first iteration)
- N°211 coded 5, 2 ème escadrille, GB I/38, Thionville Basse-Yutz, March 1933 (badge "Gaul's Head" 2 nd iteration)
- N°2042 coded 3, 1 ère escadrille, GO I/33, Nancy, October 1932 to March 1937
- N.B : le 207 en rouge est bien attesté sur le fuselage, pour les deux autres ils sont possibles (selon normes). Par erreur le n°201 rouge a été mis en place du 211 ...